반응형
너비우선탐색(BFS) 이란?
- Breadth First Search의 약자
- 어떠한 노드에서 인접한 노드들부터 순차적으로 방문하는 탐색방법
장점
- 최단경로를 보장한다.
단점
- 경로가 길 경우에는 많은 기억공간을 요구한다.
- 무한그래프의 경우 해가 없는경우에는 찾지도, 끝내지도 못하는 상황이 발생할 수 있다.
- 유한그래프의 경우 해가 없는 경우에 모든 그래프를 탐색한 후 실패로 끝난다.
- 깊이우선탐색(DFS)보다 구현이 복잡하다.
사용사례
- 최단경로를 찾고 싶을때
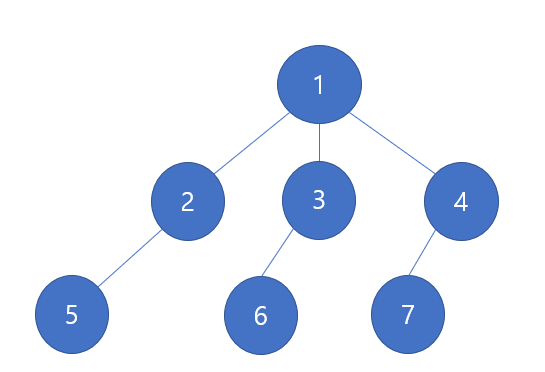
실행순서 예시
구현코드
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size;
int command;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
size = sc.nextInt();
command = sc.nextInt();
Queue queue = new Queue(size);
queue.init();
for(int i =0; i<command;i++){
int startIdx = sc.nextInt();
int endIdx = sc.nextInt();
queue.addPoint(startIdx-1,endIdx-1);
}
queue.BFS(0);
}
}
class Queue{
List<Integer>[] queue;
Boolean[] visit;
List<Integer> store = new ArrayList<>();
int size;
public Queue(int size){
this.queue = new ArrayList[size];
this.visit = new Boolean[size];
this.size = size;
}
public void init(){
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
queue[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
visit[i] = false;
}
}
/**
*
* @param startPoint 시작지점
* @param endPoint 도착지점
*/
public void addPoint(int startPoint,int endPoint){
queue[startPoint].add(endPoint);
queue[endPoint].add(startPoint);
}
public void BFS(int startIdx){
store.add(startIdx);
while(store.size() > 0){
int temp = store.remove(0);
if(visit[temp] == false){
visit[temp] = true;
Collections.sort(queue[temp]);
queue[temp].stream().forEach(integer -> {
if(visit[integer] == false){
store.add(integer);
}
});
System.out.println((temp+1) + "방문");
}
}
}
}
반응형
'컴퓨터공학 기초 > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 이진탐색트리(BST) 란 ? (0) | 2020.02.09 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘] 깊이우선탐색(DFS)이란 ? (0) | 2020.02.05 |
| [알고리즘] 스택(Stack)이란 ? (0) | 2020.02.03 |
| [알고리즘] 퀵정렬이란 ? (0) | 2020.02.02 |
| [알고리즘] 버블정렬이란 ? (0) | 2020.02.01 |



댓글